In recent years, Industry 4.0 has emerged as a transformative force in the manufacturing sector. This concept, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, refers to the integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and Cloud Computing into manufacturing processes. The goal of Industry 4.0 is to create a more interconnected and efficient manufacturing ecosystem, where data can be collected and analyzed in real-time to optimize production and reduce costs.
The manufacturing sector is no stranger to economic challenges, and recessions can be particularly tough on manufacturers. During a recession, demand for goods and services typically decreases, leading to reduced revenue and profits for businesses. This shift can result in layoffs, bankruptcies, and a general slowdown in economic activity. However, the manufacturing sector has historically shown resilience during times of economic uncertainty, due in part to its ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how Industry 4.0 can help manufacturers not only weather recessions but also emerge stronger on the other side. By adopting the latest technologies and tools, manufacturers can enhance their resilience and pivot their operations toward growth. We’ll discuss specific examples of how Industry 4.0 is changing the manufacturing landscape and explore the potential benefits for businesses of all sizes.
The Resilience of the Manufacturing Sector in Recessions
The manufacturing sector has shown remarkable resilience during past economic downturns. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, manufacturing output initially fell sharply, but it recovered more quickly than other sectors, and by 2010, it had surpassed pre-crisis levels. Manufacturers are often able to adapt their operations to meet changing market conditions, whether that means reducing costs, diversifying their product lines, or exploring new markets.
Manufacturing is also a critical part of many supply chains, which means that disruptions can have ripple effects throughout the economy. As a result, policymakers often focus on supporting the manufacturing sector during recessions to promote economic stability.
However, not all manufacturers are equally resilient, and some may struggle more than others during a recession. Here’s where Industry 4.0 can help: by adopting the latest technologies and tools, manufacturers can enhance their resilience and position themselves for long-term success.
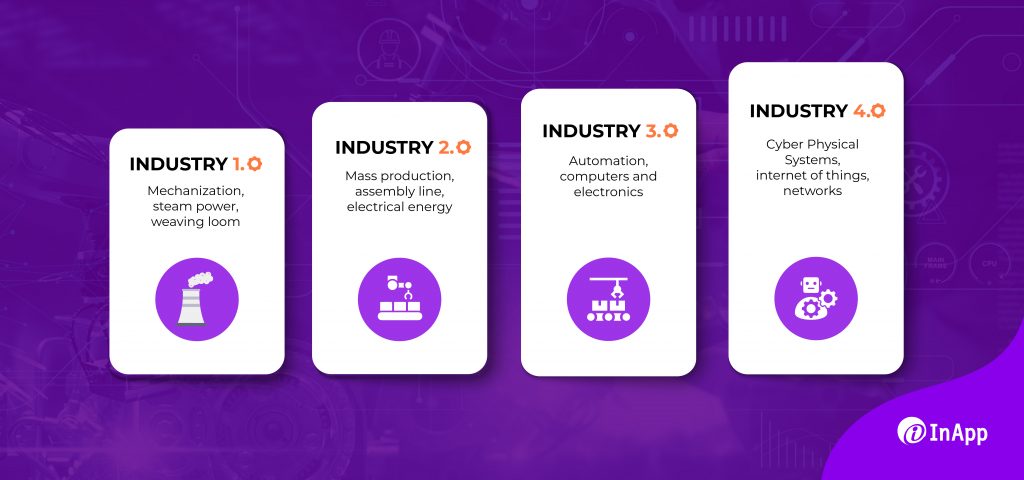
What is Industry 4.0?
At the risk of oversimplifying a complex subject, Industry 4.0 is essentially about automating business ecosystems with the help of emerging technologies such as the Industrial IoT (IIoT), big data (and analytics), cloud computing, robotics, digital twins, artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and cybersecurity, to name a few.
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, refers to the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, the IoT, robotics, and data analytics into industrial processes to predict, control, and plan business outcomes.
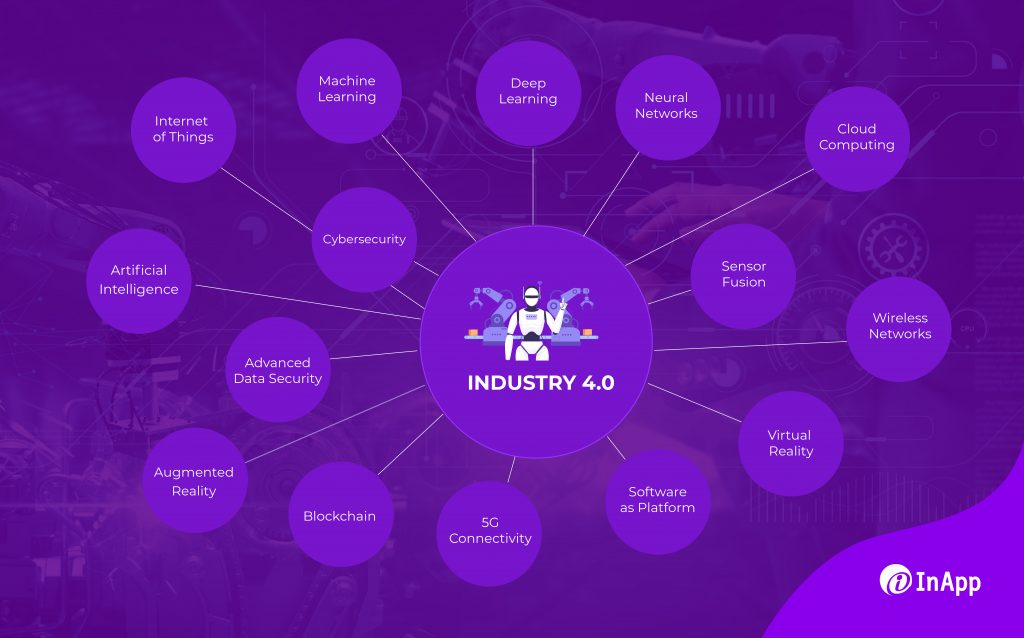
Industry 4.0 is characterized by using cyber-physical systems, which are systems that integrate physical processes with digital technologies. This integration enables industries to optimize their operations, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve productivity. These systems are designed to collect, analyze, and communicate data in real time, allowing for real-time decision-making and automation of industrial processes.
Some of the key technologies that fall under the Industry 4.0 umbrella include:
1. The Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data. In manufacturing, IoT can be used to monitor machines and equipment in real time, allowing manufacturers to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to learn and make decisions based on data. In manufacturing, AI can be used to optimize production processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve product quality.
3. Robotics: Robotics refers to the use of automated machines to perform tasks that humans typically do. In manufacturing, robotics can be used to automate repetitive or dangerous tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-value activities.
4. Cloud Computing: Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, allowing users to access and store data and applications remotely. In manufacturing, cloud computing can be used to store and analyze large amounts of data, enabling real-time monitoring of production processes and optimization of workflows.
5. Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process of building three-dimensional objects by adding layer upon layer of material. Additive manufacturing can be used to create complex parts quickly and with less waste than traditional manufacturing methods.
By adopting these technologies and integrating them into their operations, manufacturers can create a more efficient, flexible, and resilient production process that can shift quickly to changing market conditions. This adaptability can be particularly valuable during recessions, when demand for certain products may decrease, and manufacturers need to find ways to reduce costs and optimize their workflows.
Industry 4.0 in Practice: Examples from the Manufacturing Sector
A generational shift by the application of Industry 4.0 has revolutionized industries such as logistics and transportation, healthcare, manufacturing, and automotive to name a few. This paradigm shift has become even starker with the onset of Covid-19 as evidenced by this article from McKinsey, which shows companies that had already scaled their digital technologies before the pandemic clearly handled the crisis better than those who had not initiated the journey.
The benefits of Industry 4.0 are not just theoretical. Many manufacturers have already begun to adopt these technologies and are seeing real-world results. Here are a few examples:
1. Predictive Maintenance: By using IoT sensors to monitor machines and equipment in real time, manufacturers can identify potential issues before they become major problems. This data can help prevent unplanned downtime and reduce maintenance costs. For example, Schindler Elevator Corporation has implemented an IoT-based predictive maintenance system for its elevators and escalators, which has reduced downtime by 20% and maintenance costs by 25%.
2. Quality Control: AI can analyze data from sensors and other sources to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate quality issues. As a result, manufacturers can catch defects earlier in the production process and improve overall product quality. For example, Siemens uses AI-powered image recognition technology to inspect turbine blades for defects, resulting in a 98% reduction in inspection time.
3. Flexibility: Additive manufacturing can produce small batches of complex parts quickly and with less waste than traditional manufacturing methods, helping manufacturers respond quickly to changes in demand or customer needs. For example, Nike uses additive manufacturing to produce custom shoe components on demand, allowing customers to create personalized shoes that are tailored to their exact needs.
4. Supply Chain Optimization: Cloud computing can store and analyze large amounts of data from across the supply chain, allowing manufacturers to optimize their workflows and reduce costs. For example, Rolls-Royce uses cloud-based analytics to monitor its supply chain and identify potential bottlenecks, allowing the company to make adjustments in real time and minimize disruptions.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Industry 4.0
While the benefits of Industry 4.0 are clear, manufacturers should be aware of some challenges and considerations when implementing these technologies. Here are a few:
1. Cost: Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies can require a significant upfront investment in equipment, software, and training. This outlay can be a barrier to adoption for small and medium-sized manufacturers with limited resources.
2. Data Privacy and Security: IoT and cloud computing technologies rely on the collection and sharing of data, which can raise concerns about data privacy and security. Manufacturers need to be diligent about protecting their data and ensuring that they comply with applicable regulations.
3. Workforce Training: Adopting Industry 4.0 technologies often requires new skills and training for workers. Manufacturers need to ensure that their employees have the necessary skills to operate and maintain these systems.
4. Integration: Implementing multiple Industry 4.0 technologies requires careful integration to ensure that they work seamlessly together. Manufacturers need to have a clear plan for incorporating these technologies into their existing systems and workflows.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of Industry 4.0 are significant, and companies that can overcome these obstacles will be better positioned to weather recessions and emerge stronger on the other side. By adopting these technologies and using them to enhance their resilience and pivot towards growth, manufacturers can stay competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
The Way Forward
From drones to digital sensors; digital twins to 3D printing; AI to big data analysis – the future is here and only beginning to reveal itself. Those who will write its history will be the ones that were amenable to change while being bold with their plans, even within the limitations of their current capabilities.
While some challenges and considerations come with implementing Industry 4.0 technologies, the benefits are significant. Manufacturers that can overcome these obstacles will be better positioned to weather recessions and emerge stronger on the other side. By using these technologies to pivot towards growth, manufacturers can stay competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
Ultimately, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is not only important for navigating recessions but also for staying competitive in the long term. The potential benefits include increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved quality, and greater flexibility. As such, it is crucial for manufacturers to embrace Industry 4.0 and leverage these technologies to enhance their resilience and drive growth.
