Artificial Intelligence is making businesses improve their products and customer experience based on predictive analytics tools. However, it’s a long and complex process. Not all organizations can venture into building the AI process in-house, requiring a huge investment. Here comes Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AIaaS)! AIaaS let you use AI functionalities without developing in-house expertise. InApp’s concise and two-minute read infographic introduces AIaaS.
Artificial Intelligence as a Service | AIaaS
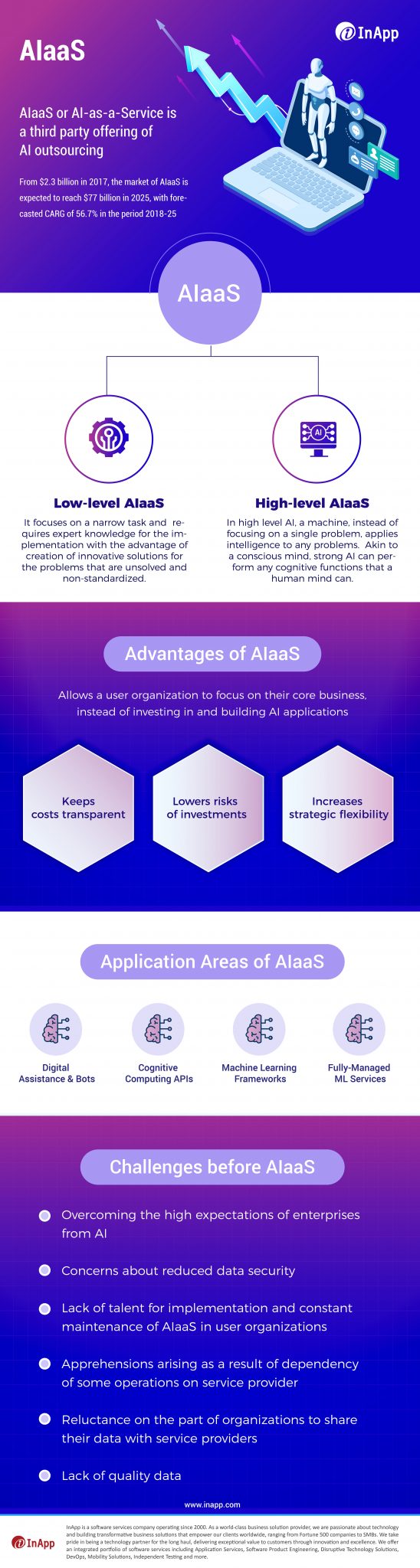
AIaaS or AI-as-a-Service is a third-party offering of AI outsourcing. From $2.3 billion in 2017, the market of AIaaS is expected to reach $77 billion in 2025, with a forecasted CAGR of 56.7% in 2018-25.
Low-level AIaaS: It focuses on a narrow task and requires expert knowledge for the implementation with the advantage of the creation of innovative solutions for problems that are unsolved and non-standardized.
High-level AIaaS: In high-level AI, a machine, instead of focusing on a single problem, applies intelligence to any problem. Akin to a conscious mind, strong AI can perform any cognitive functions that a human mind can.
What are the Advantages of AIaaS?
Allows a user organization to focus on its core business, instead of investing in and building Artificial Intelligence applications
- Keeps costs transparent
- Lowers risks of investments
- Increases strategic flexibility
What are the Application Areas of AIaaS?
- Digital Assistance & Bots
- Cognitive Computing APIs
- Machine Learning Frameworks
- Fully-Managed ML Services
What are the Challenges of AIaaS?
- Overcoming the high expectations of enterprises from Artificial Intelligence
- Concerns about reduced data security
- Lack of talent for implementation and constant maintenance of AIaaS in user organizations
- Apprehensions arising as a result of dependency of some operations on the service provider
- Reluctance on the part of organizations to share their data with service providers
- Lack of quality data